Selling a Put is opposite of buying a Put. An investor buys Put when he is bearish on a stock. An investor Sells Put when he is Bullish about the stock – expects the stock price to rise or stay sideways at the minimum. When you sell a Put, you earn a Premium (from the buyer of the Put). You have sold someone the right to sell you the stock at the strike price. If the stock price increases beyond the strike price, the short put position will make a profit for the seller by the amount of the premium, since the buyer will not exercise the Put option and the Put seller can retain the Premium (which is his maximum profit). But, if the stock price decreases below the strike price, by more than the amount of the premium, the Put seller will lose money. The potential loss being unlimited (until the stock price fall to zero).
When to Use: Investor is very Bullish on the stock / index. The main idea is to make a short term income.
Risk: Put Strike Price – Put Premium.
Reward: Limited to the amount of Premium received.
Breakeven: Put Strike Price – Premium
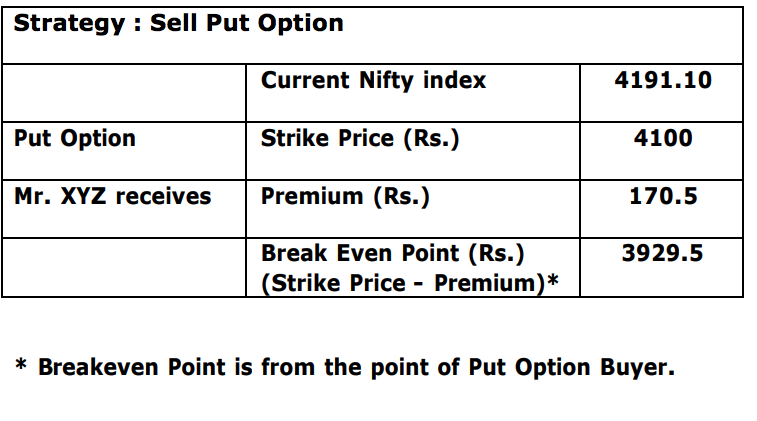
Example Mr. XYZ is bullish on Nifty when it is at 4191.10. He sells a Put option with a strike price of Rs. 4100 at a premium of Rs. 170.50 expiring on 31st July. If the Nifty index stays above 4100, he will gain the amount of premium as the Put buyer won’t exercise his option. In case the Nifty falls below 4100, Put buyer will exercise the option and the Mr. XYZ will start losing money. If the Nifty falls below 3929.50, which is the breakeven point, Mr. XYZ will lose the premium and more depending on the extent of the fall in Nifty.


ANALYSIS : Selling Puts can lead to regular income in a rising or range bound markets. But it should be done carefully since the potential losses can be significant in case the price of the stock / index falls. This strategy can be considered as an income generating strategy.